-
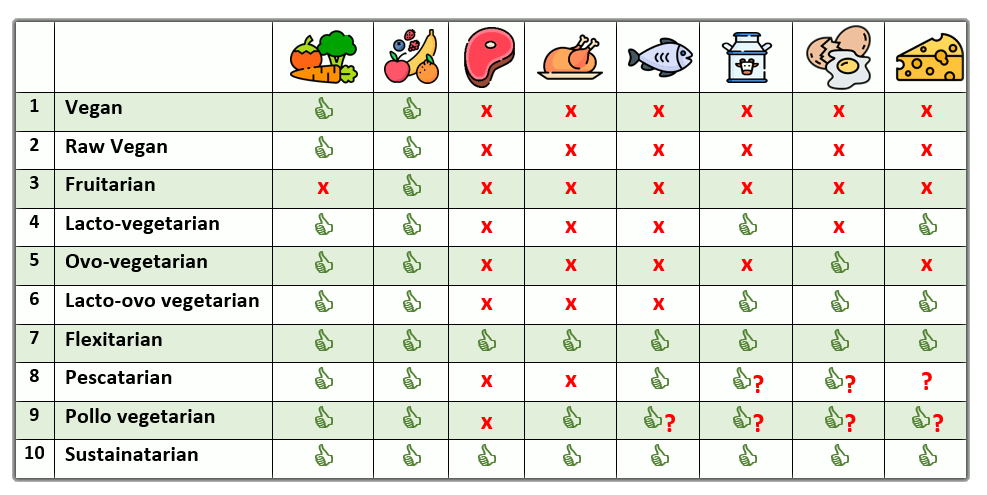
Classic Vegetarian DietClassic Vegetarian Diet, is a plant-centric diet which excludes all types of animal and fish proteins, as well as dairy and its sub-products.
-
Vegan DietA Vegan Diet is one of the most restrictive vegetarian diets. It is a strictly plant-based diet that completely excludes all animal products, such us: meat, fish, dairy, eggs, honey, and gelatin.
-
Raw Vegan DietIf a Vegan Diet is an extreme form of Vegetarian Diet, then the Raw Vegan Diet is an extreme form of Vegan Diet itself. Raw-Veganists eat a strictly plant-based uncooked or minimally heated foods, typically not exceeding a temperature of 118°F (48°C). Raw-Veganists believe that raw foods are more nutritionally reach and easy to digest, as cooking destroys enzymes and vitamins in food.
-
FruitarianFruitarianism is a form of highly restricted raw vegan diet, centered around fruit consumption. One of the famous followers of this diet was Apple's Founder and CEO Steve Jobs. Many Fruitarian consume small amounts of vegetables, but most avoid nuts (even in raw form).
-
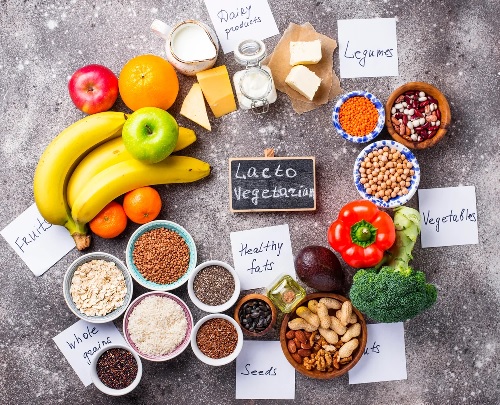
Lacto-Vegetarian DietLacto-vegetarians are the classic a plant-based Vegetarians who allowed to consume dairy as additional source of protein. That includes milk, butter, cheese, yogurt, and ice cream. The largest groups of Lacto-vegetarians are the followers of Hinduism and Sikh religions.
-
Ovo-Vegetarian DietOvo-vegetarians are the vegetarians who is allowed to consume eggs and eggs-based products. Like classic Vegetarians Ovo-vegetarians avoid meats and other animal products.
-
Lacto-Ovo Vegetarian DietLacto-Ovo Vegetarians combine dietary principles of Lacto-Vegetarians with Ovo-Vegetarian Diet. They belived to be the most popular form of vegetarianism. While Lacto-Ovo vegetarians strictly avoid all forms of animal proteins (meat, poultry, seafood, and fish) they are allowed to eat a dairy and eggs.
-
Flexitarian DietThe Flexitarian Diet, often-times also called Semi-Vegetarian Diet (SVD), is a primarily plant-based diet. Meat consumption in small quantities is allowed but restricted to occasional meals, often including poultry or fish, and may exclude red meat entirely. Depending on person, dairy products and eggs may be included in a semi-vegetarian diet.
-
Pescatarian DietPescatarians are the Vegetarians who eat fish and seafood. Some pescatarians may eat dairy and eggs. Because of these reasons, Pescatarian Diet is considered to be a special form of Flexitarian Diet described above.
-
Pollo Vegetarian DietPollo Vegetarian Diet is another special form of flexitarian diet, which relaxes Vegetarian principles towards consumption of chicken and other types of poultry (turkey, ducks and other fowl). Some Pollo Vegetarians make one step further adding seafood, fish, eggs, and dairy products to their diet, making it very close to typical flexitarian diet.
-
Sustainatarian DietSustainatarian stands for Sustainable vegetarian diet. Main philosophy of this diet is based on partaking of food that is sustainably sourced to reduce food waste and to lessen our impact on the planet. Sustainatarian food includes, for example, vegetarian fare, sustainably caught seafood, or sustainably raised, or game, meat.